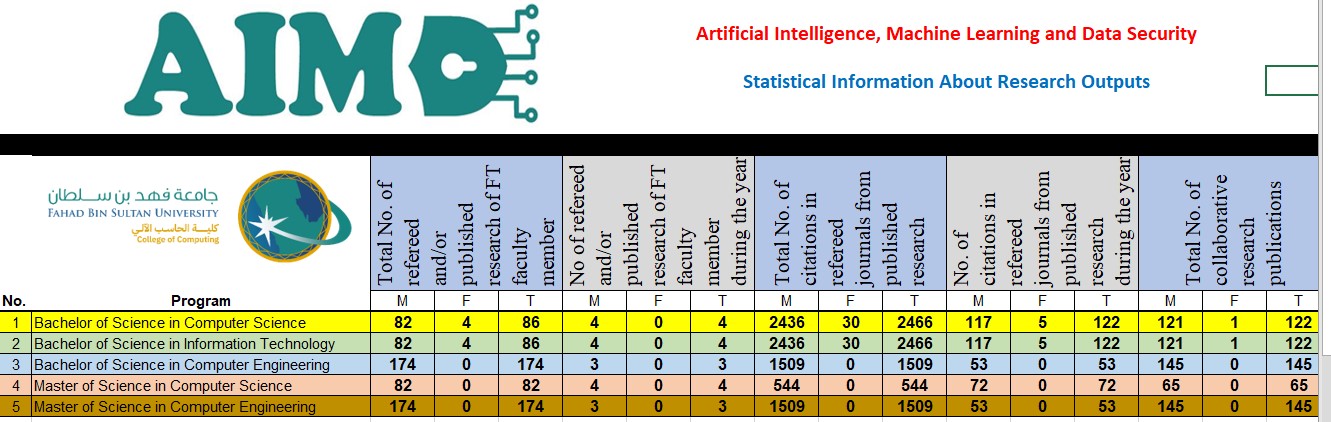
Researh Outputs:
Excel file provides statistical information about the research outputs for (Year 22-23 and Year 23-24).
Major Researh Projects:
Currently, three main projects are under-processing as follows:
|
No. |
Domain |
AI Research Group |
|
1 |
Deep Learning |
Title: MCD-StrBeh: Deep Learning Based System for Malicious Clones Detection Based on Structural and Behavioral Similarities |
|
Abstract Detection of similarity is vital to prevent spreading of malicious codes in cybersecurity domain. Attackers can tamper the original code of malicious malware to deceive detection systems. This leads to big damage to information systems. In this work, a deep learning based system (called MCD-StrBeh) is presented to detect similarities between original malicious codes and modified ones. The architecture of the proposed system consists of six components. Tokenizer takes source code as an input and extracts a series of tokens. The tokens are converted into a directed graph by the graph generator component. The tracker forms a traces on the generated graph. Patterns within a traces are detected by pattern detector component. The detected patterns are used as inputs to the similarity matrix former to extract features. Finally, the score of the similarity is measured by the similarity calculator component, where Jaccard distance is used in this context. |
||
|
2 |
Deep Learning |
Title: An Augmentation-Based System for Diagnosing COVID-19 Using Deep Learning |
|
Abstract Recently, due to the dangerous spread of COVID-19, there has been strong competition among computer science researchers within the scientific research community to employ deep learning for the development of intelligent medical systems that diagnose this illness. Enhancing accuracy is considered the most important objective, and augmentation techniques are used in this context. This work addresses two main issues related to applying augmentation on X-ray and CT-scan images: losing the positional information of augmented medical images and the integration of extracted features while scanning them. The use of the Vision Transformer Structure, supported by a Position-Aware Embedding (PAE) method, is proposed to deal with these issues. Moreover, in this study, a student–teacher-based approach was adopted to enable considerable resistance against training on a small batch of training images. Due to the sensitivity of medical data, preserving the privacy of patients was taken into account by using a pseudonym-based anonymity approach. After evaluations based on accuracy, precision, recall, and specificity metrics, the results showed that the proposed system has a high-level capability to predict class images (X-ray or CT-scan) as well as considerable resistance against training on small medical images.
|
||
Partnerships:
- IIE-SRF American Institution.